IV. 2MASS Data Processing
1. Processing Pipeline Overview
a. Data Processing Strategy
Data processing for 2MASS was conducted using the highly automated 2MASS Production Processing System (2MAPPS) which converted each night's raw imaging data from each telescope into calibrated images and extracted source lists.
Processing was done in two stages. Preliminary processing was carried out while the Survey was ongoing using a version of 2MAPPS (v2.x) that was allowed to evolve and improve continuously as our knowledge of the telescopes, cameras, detectors, atmosphere and the near infrared sky improved. The 2MASS Sampler, First and Second Incremental Data Releases were derived from the results of the preliminary data processing. A second, complete reprocessing of all Survey data following the completion of the Survey observations was performed, and enabled all data to be reduced using a single, stable software platform, 2MAPPS v3.0. 2MAPPS v3.0 incorporated lessons learned during the preliminary processing and feedback provided by users of the Incremental Data Release products. It also made use of reference datasets not available earlier, such as the Tycho 2 astrometric reference catalog, and information gathered from analysis of the complete survey data set. 2MAPPS v3.0 also contained numerous upgrades that improved the general quality and yield of data from the survey. Finally, 2MAPPS v3.0 included more extensive Quality Assurance tied explicitly to metrics derived from scientific investigations of the data.
An overview of the basic processing steps are given below in Section b, and a summary of the improvements incorporated into 2MAPPS v3.0 for final data processing are given in Section c. Sections IV.2-10 provide a detailed description of data processing algorithms and results.
b. Nightly Data Processing Steps
Approximately 17 GB of raw digital image data were acquired each clear night at the 2MASS observatories. These data were written to DLT tape (one tape per observatory per night) and transported to the Infrared Processing and Analysis Center (IPAC). At IPAC, the observatory data tapes were read and validated, and the data were reduced using the 2MASS Production Processing System (2MAPPS). 2MAPPS was designed to exploit the Survey's innovative data acquisition techniques to produce image, point and extended source data.
The 2MAPPS High Level Flowchart (Figure 1) illustrates the basic components of the 2MAPPS system. Data from one night and one observatory were processed as a unit. For each telescope-night, each 1° calibration or 6° survey scan was processed individually, with the J, H and Ks frame data in each scan processed in parallel. Scan data processing within 2MAPPS was a linear process with the output of each step being the input for each subsequent step. Iterations were held to a minimum for efficiency.
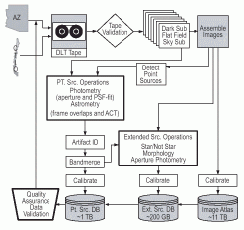
|
| Figure 1 |
The basic scan processing steps are the same for calibration and survey scans, and are as follows:
- Each "Read 1" (R1; 51 ms exposure) and "Read2-Read1" (R2-R1; 1.3 s exposure) data frame from a survey or calibration scan is dark-subtracted, flat-fielded and sky-illumination corrected (IV.2)
- Point sources are first detected and measured on each corrected frame to provide first-order position reconstruction and frame-to-frame offsets, as well as photometry for the brightest stars
- The frames are then combined into the Atlas Images (IV.3)
- Point sources are detected from the Atlas Images for maximum sensitivity (IV.4.a)
- Positions and brightnesses are measured for each point source, and artifacts produced from bright stars are then identified in the source lists (IV.4)
- Sources from the three bands are then "merged" into single sources (IV.4.e), and final position reconstruction is carried out relative to the Tycho 2 catalog (IV.6)
- Each bandmerged point source is then scrutinized to determine if it is actually resolved. Extended source candidates are characterized, deriving brightness and basic shape information. (IV.5)
Once all scan processing for data taken at one observatory in one night is completed, post-scan-processing is carried out. The nightly post-scan-processing steps include:
- Extract and assess photometric calibration from calibration observations, and apply photometric calibrations to point and extended sources and Atlas Images for photometrically acceptable periods (IV.8)
- Verify the processing and science quality of the data (IV.10)
- Load source lists, images and scan information data that meet minimum Quality Assurance standards into Working Databases
Pipeline processing yields lists of band-merged, photometrically and astrometrically calibrated point and extended source "detections" from each Survey and Calibration scan. These lists are accumulated into the Point Source and Extended Source Working Databases from which the 2MASS Point and Extended Source Catalogs are drawn. The process of generating the Catalogs from the Working Databases is described in Section V.
Final 2MASS Survey data processing using 2MAPPS v3.0 began on 2 August 2001 and was completed on 6 February 2002. All Survey data acquired under photometric conditions were included in the final processing. This included scans of 70,712 Tiles taken on 1415 survey nights (691 northern and 750 southern) spanning 7 June 1997 UT to 15 February 2001 UT. The final processing Working Databases contain 1,314,981,867 Point and 2,590,500 Extended source extractions, and an Atlas of 4,879,128 calibrated FITS images
c. Improvements Incorporated in Final Processing (2MAPPS v3.0)
The following list summarizes the major improvements relative to earlier versions that were incorporated in 2MAPPS v3.0. Because of these improvements, the quality of the 2MASS All-Sky Release data products surpass those from the Incremental Releases, and the All-Sky products are designed to supersede the products from the earlier releases.
- Instrumental Calibration
- Use of 2-dimensional saturation map for each array. A constant saturation threshold value for all pixels in each array was used during preliminary processing.
- Best time-Dependent Canonical Dark Images and Flat-field Images generated using all survey data. Flat-field images incorporate corrections for cross-scan biases observed in point source photometry.
- Atlas Images
- Meteor trail detection and blanking for Atlas Images implemented.
- Improved frame background "tilting" in Atlas Image construction to deal with high-order spatial structure in frame backgrounds.
- Atlas Image backgrounds provide better representation of true Poisson noise for setting detection thresholds. Result is that Atlas Image backgrounds may not match smoothly in-scan.
- Single pixel coverage allowed into Atlas Images to minimize "holes".
- Point Source Characterization
- Improved noise estimator for establishing source detection thresholds. Less sensitive to low-frequency background structure.
- Saturated R1 star detection, centroiding and brightness estimation implemented using 1-dimensional radial profile fitting.
- Improved set of point-spread-functions and variance maps developed for all arrays and all hardware periods. Results are better uncertainty estimation vs. brightness and chi-squared statistical distributions.
- Used seeing-dependent look-up table values for aperture photometry curve-of-growth and normalization of R1/R2 photometry. This minimized errors due to small number statistics in empirical derivation on scan-by-scan basis.
- Extended Source Characterization
- Higher-order background fits used for extended sources measurements to mitigate H-band airglow structure.
- Switched from magnitude thresholding in extended source identification to SNR thresholding. Thus, the extended source processing operated on fainter sources when the conditions warranted.
- Training set for decision tree used for extended source classification expanded using data from full survey.
- Improved robustness of photometry in crowded regions by using an iterative fit/subtraction of foreground stars.
- Galaxy completeness improved in high source density regions by ~0.5 mag through better multiple star discrimination.
- Specialized processing for Large Galaxies.
- Extended source coverage maps generated.
- Astrometry
- Higher density Tycho 2 Catalog used a primary astrometric reference catalog.
- Measure and monitor focal plan distortion and included in source astrometric reconstruction.
- Used position/uncertainty correction tables derived from preliminary processing to propagate astrometric solutions across scan boundaries. This improves performance in regions with low astrometric reference and 2MASS star densities.
- Artifact Identification
- Improved identification of artifacts from bright star artifact enabled by saturated star brightness estimation and updated geometric algorithm parameter derivation.
- Less conservative flagging of bright star artifacts in high source density regions.
- Photometric Calibration
- Derived improved secondary standard list compiled from full survey. Best possible internal consistency and rejection of variable stars.
- Time variable atmospheric extinction model used (varies by month) derived from global calibration solutions from entire survey.
- Employed higher order fits to nightly zero point offset measurements. Piece-wise fit used in the J-band, linear fits used for the H and Ks bands). These fits produce lowest overall residuals for calibration stars.
- Minor Planet Identification
- Newest ephemerides used for asteroid and comet identification.
- Planetary satellites identified.
- Quality Assurance
- Greatly expanded automated quality review of nightly processing. Introduction of QA diagnostics based on scientific metrics.
[Last Update: 10 March 2003, by R. Cutri]
Previous page. Next page.
Return to Explanatory Supplement TOC Page.